Search: keyword:fuzzy
|
|
| Displaying 21-28 of 28 results found.
|
( prev ) page 1 2 3
|
|
|
Sort:
id
Format:
long
Filter:
(all | no meta | meta)
Mode:
(words | no words)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| BP865 |
| The class of included examples is distractingly irrelevant to the solution vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
Left examples have keyword "distractingworld" on the OEBP.
This is different than the kind of distraction mentioned at noisy, which means there are details that are irrelevant to the solution changing between examples.
To label a BP "distractingworld" is to judge that the type of examples are more specific than should have been necessary to communicate the same general solution idea--this involves separating out which ideas are the nice ideas the BP really ought to have been about, and which ideas seem unimportant and irrelevant. On the other hand, to label a BP "noisy" is just to notice there are extra properties varying that are independent of the solution property. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Distractingworld BPs are often arbitrary.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP860 BP861 BP862 BP863 BP864 * BP866 BP867 BP868 BP869 BP870
|
|
|
EXAMPLE
|
BP1105 was created as an extreme example of this. All images in that BP show the same distractingly detailed background, irrelevant to the solution. |
|
|
KEYWORD
|
stub, fuzzy, abstract, subjective, meta (see left/right), links, keyword
|
|
|
WORLD
|
bp [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP894 |
| Examples fit solution (once it is known) relatively obviously vs. examples fit solution in subtle or complex, harder-to-see ways. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
One left and one right example with each solution are shown for help.
This BP is fuzzy for multiple reasons. How obvious it is that an example fits a rule is subjective. Also, somebody could read the simplicity of all included examples as part of a Bongard Problem's solution. For example, the more obvious version of "square number of dots vs. non-square number of dots" could be interpreted as "square small number of dots arranged in easy-to-read way vs. non-square small number of dots arranged in easy-to-read way."
Whether this Bongard Problem solution would categorize an image of itself left or right depends on the difficulty of the solutions of the mini-Problems. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
See keyword help.
See keyword hardsort.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP889 BP890 BP891 BP892 BP893 * BP895 BP896 BP897 BP898 BP899
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
fuzzy, abstract, notso, subjective, meta (see left/right), miniproblems, creativeexamples, presentationmatters, assumesfamiliarity, structure, contributepairs
|
|
|
WORLD
|
boxes_bpimage_three_per_side [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP895 |
| Meta Bongard Problems that sort Bongard Problems based on other information than just their solutions (e.g. what format the Bongard Problem is, or what specific examples are shown in it) vs. Meta Bongard Problems that sort Bongard Problems purely based on solution. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
Left-sorted Bongard Problems have the keyword "presentationmatters" on the OEBP.
Right-sorted Bongard Problems have the keyword "presentationinvariant" on the OEBP.
Meta Bongard problems that sort Bongard Problems purely based on their solutions usually have two versions in the database: one that sorts images of Bongard Problems and one that sorts links to pages on the OEBP. If both versions exist, users should make them cross-reference one another. (Meta Bongard Problems that sort images of Bongard Problems have the keyword miniproblems, whereas meta Bongard Problems that sort links to OEBP pages have the keyword links.)
For meta-pages on the OEBP that sort other pages on the OEBP (keyword links), "presentationmatters" means factoring in content like the BP number, the currently uploaded examples, the wording of the title, the description, and so on, rather than just the solution (that is, how the page would sort all potential examples). This is unusual.
"One solution vs. multiple solutions" (BP828) seems like a border-case. - Aaron David Fairbanks, Aug 01 2020 |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
See BP1010 (projectionmatters versus 3d) for a similar idea: there 2D representations are to 3D objects as here Bongard Problems are to Bongard Problem solutions.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP890 BP891 BP892 BP893 BP894 * BP896 BP897 BP898 BP899 BP900
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
fuzzy, meta (see left/right), links, keyword, right-self, sideless, metameta, right-it, dependence, presentationinvariant
|
|
|
WORLD
|
metabp [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Jago Collins
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP939 |
| Optical illusions vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1002 |
| Vaguely self-similar (looks like self-similar fractal after one iteration) vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
See BP1004 for a Problem about conceptual self-similarity instead of visual self-similarity.
See BP188 for a similar Problem restricted to shape outlines made of shape outlines.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP997 BP998 BP999 BP1000 BP1001 * BP1003 BP1004 BP1005 BP1006 BP1007
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
easy, nice, fuzzy, abstract, anticomputer, concept, traditional
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
fractal (info | search),
recursion (info | search),
self-reference (info | search),
similar_shape (info | search),
similar (info | search)
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1111 |
| Bongard Problem requires solver to already be interpreting all examples in a specific way for the answer to seem simple vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
Left-sorted Bongard Problems have the keyword "assumesfamiliarity" on the OEBP.
Sometimes all the examples in a Bongard Problem need to be interpreted a certain way for the Bongard Problem to make sense. Only once the representation is understood, the idea seems simple.
For example, all meta Bongard Problems (Bongard Problems sorting other Bongard Problems) assume the solver interprets the examples as Bongard Problems.
TO DO: Maybe it is best to stop putting the label "assumesfamiliarity" on all meta-Bongard Problems. There are so many of them. It may be better to only use the "assumesfamiliarity" keyword on meta-BPs for a further assumption than just that all examples are interpreted as Bongard Problems. - Aaron David Fairbanks, Feb 11 2021 |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Many Bongard Problems in which all examples take the same format (keyword structure) assume the solver already knows how to read that format.
Some Bongard Problems assume the solver will be able to understand symbolism that is consistent between examples (keyword consistentsymbols).
Bongard Problems tagged math often assume the solver is familiar with a certain representation of a math idea.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP1106 BP1107 BP1108 BP1109 BP1110 * BP1112 BP1113 BP1114 BP1115 BP1116
|
|
|
EXAMPLE
|
BP1032: The solution should really read "Assuming all images are Bongard Problems sorting each natural number left or right ..." This Bongard Problem makes sense to someone who has been solving a series of similar BPs, but otherwise there is no reason to automatically read a collection of numbers as standing for a larger collection of numbers. |
|
|
KEYWORD
|
fuzzy, meta (see left/right), links, keyword
|
|
|
WORLD
|
bp [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1158 |
| Bongard Problems in which each example communicates a rule vs. other Bongard Problems. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
Left-sorted Bongard Problems have the keyword "rules" on the OEBP.
In the typical "rules" Bongard Problem, it is possible to come up with many convoluted rules that fit each example, but the intended interpretation is the only simple and obvious one.
Since it is difficult to communicate a rule with little detail, "rules" Bongard Problems are usually infodense.
Typically, each example is itself a bunch of smaller examples that all obey the rule. It is the same as how a Bongard Problems relies on many examples to communicate rules; likely just one example wouldn't get the answer across.
On the other hand, in BP1157 for example, each intended rule is communicated by just one example; these rules have to be particularly simple and intuitive, and the individual examples have to be complicated enough to communicate them.
Often, each rule is communicated by showing several examples of things satisfying it. (See keywords left-narrow and right-narrow.) Contrast Bongard Problems, which are more communicative, by showing some examples satisfying the rule and some examples NOT satisfying the rule.
A "rules" Bongard Problem is often collective. Some examples may admit multiple equally plausible rules, and the correct interpretation of each example only becomes clear once the solution is known. The group of examples together improve the solver's confidence about having understood each individual one right.
It is common that there will be one or two examples with multiple reasonable interpretations due to oversight of the author. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
All meta Bongard Problems are "rules" Bongard Problems.
Many other Bongard-Problem-like structures seen on the OEBP are also about recognizing a pattern. (See keyword structure.)
"Rules" Bongard Problems are abstract, although the individual rules in them may not be abstract. "Rules" Bongard Problems also usually have the keyword creativeexamples.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP1153 BP1154 BP1155 BP1156 BP1157 * BP1159 BP1160 BP1161 BP1162 BP1163
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
fuzzy, meta (see left/right), links, keyword, left-self, rules
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1271 |
| Positive correlation vs. negative correlation. |
|
| ?
 | ?
 |
|
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
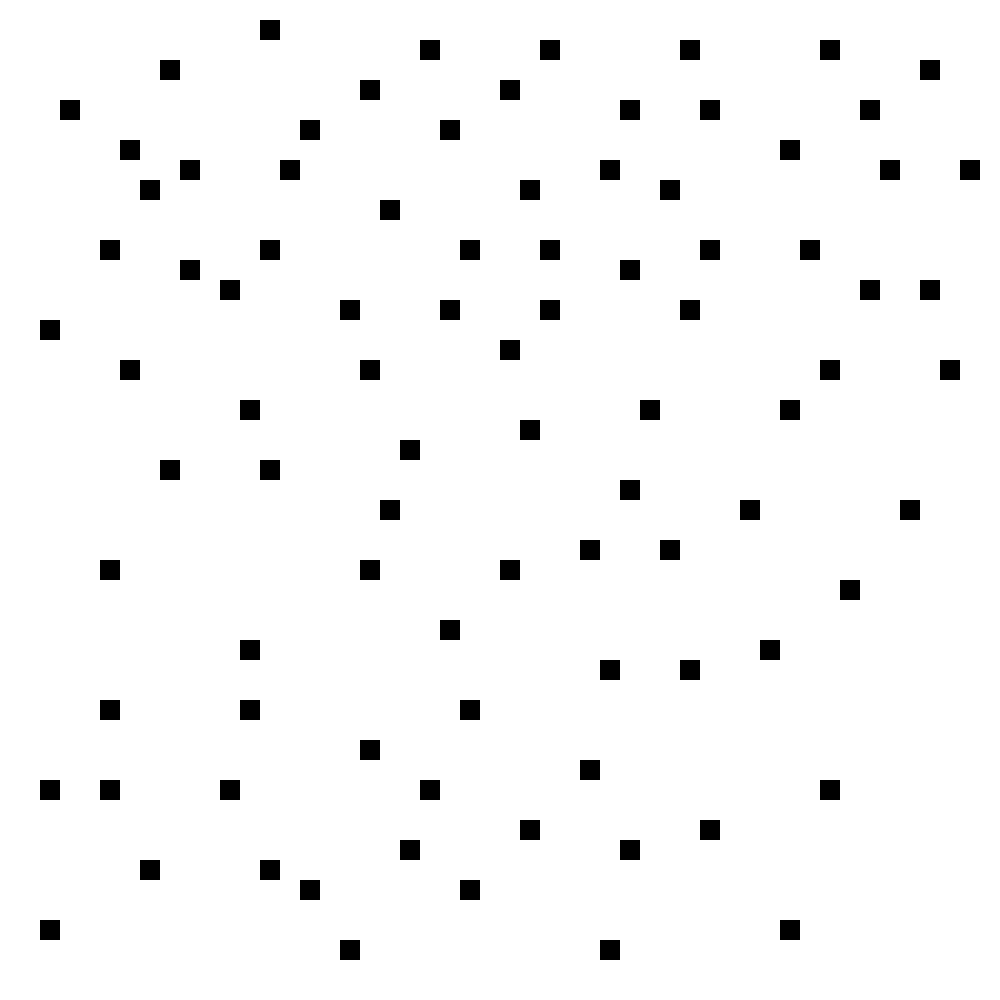
All examples in this Bongard Problem are scatter plots. Each dot represents a data point.
"Positive correlation" means that when the X value increases, the Y value tends to increase as well (in the long run), while "negative correlation" means that when the X value increases, the Y value tends to decrease. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP1266 BP1267 BP1268 BP1269 BP1270 * BP1272 BP1273 BP1274 BP1275 BP1276
|
|
|
EXAMPLE
|
Example TM4854 does not fit on either side because when the X value increases, the Y value stays the same.
Example TM4855 does not fit on either side because there is no correlation. |
|
|
KEYWORD
|
fuzzy, minimal, unwordable, teach, spectrum, dual, handed, leftright, updown, rotate, stable, hardsort, left-narrow, right-narrow
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Ben
|
| |
|
|
Welcome |
Solve |
Browse |
Lookup |
Recent |
Links |
Register |
Contact
Contribute |
Keywords |
Concepts |
Worlds |
Ambiguities |
Transformations |
Invalid Problems |
Style Guide |
Goals |
Glossary
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|