Search: keyword:unwordable
|
|
| Displaying 21-27 of 27 results found.
|
( prev ) page 1 2 3
|
|
|
Sort:
id
Format:
long
Filter:
(all | no meta | meta)
Mode:
(words | no words)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
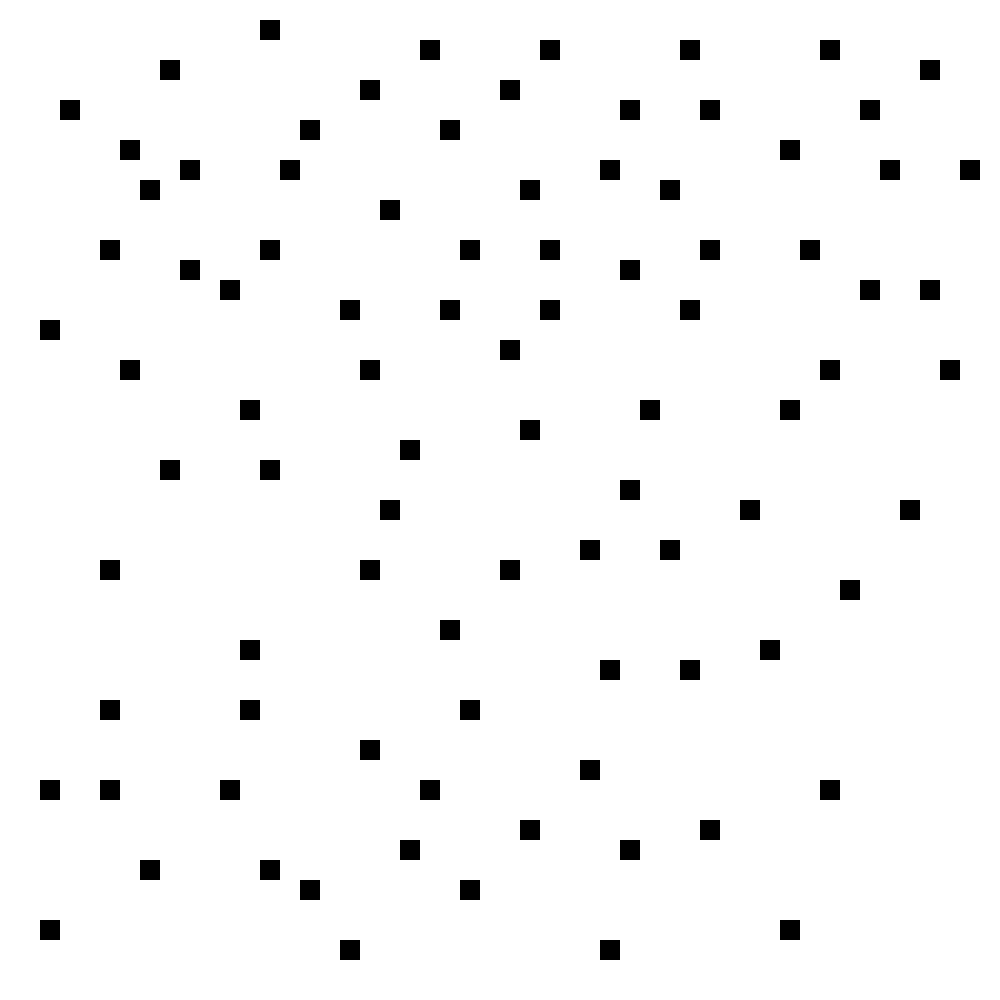
| BP1271 |
| Positive correlation vs. negative correlation. |
|
| ?
 | ?
 |
|
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
All examples in this Bongard Problem are scatter plots. Each dot represents a data point.
"Positive correlation" means that when the X value increases, the Y value tends to increase as well (in the long run), while "negative correlation" means that when the X value increases, the Y value tends to decrease. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP1266 BP1267 BP1268 BP1269 BP1270 * BP1272 BP1273 BP1274 BP1275 BP1276
|
|
|
EXAMPLE
|
Example TM4854 does not fit on either side because when the X value increases, the Y value stays the same.
Example TM4855 does not fit on either side because there is no correlation. |
|
|
KEYWORD
|
fuzzy, minimal, unwordable, teach, spectrum, dual, handed, leftright, updown, rotate, stable, hardsort, left-narrow, right-narrow
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Ben
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1275 |
| There is a way of grouping elements into (more than one) equal-sized blocks such that no block appears twice vs. there exists no such grouping. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1276 |
| Ways of representing the sequence "ABABCBACCBAC" by grouping its elements into equal-sized blocks and relabelling them (identical blocks are represented by the same element) vs. representations of different sequences. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1279 |
| Circled points are all possible vertices a square with a particular side length can take, provided that each of its corners lie on a grid point vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1280 |
| Circled points are all possible vertices a regular hexagon with a particular side length can take, provided that each of its corners lie on a grid point vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
|
|
|
|