Search: keyword:stub
|
|
| Displaying 1-10 of 37 results found.
|
( next ) page 1 2 3 4
|
|
|
Sort:
id
Format:
long
Filter:
(all | no meta | meta)
Mode:
(words | no words)
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| BP860 |
| Finitely many copies of the shape can be arranged such that they are locked together vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
This is a generalisation of BP861.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP855 BP856 BP857 BP858 BP859 * BP861 BP862 BP863 BP864 BP865
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
hard, nice, stub, precise, stretch, unstable, hardsort, challenge, creativeexamples, perfect, pixelperfect
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
tiling (info | search)
|
|
|
WORLD
|
fill_shape [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Leo Crabbe
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP969 |
| Triangle is smallest black shape vs. square is smallest black shape. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP970 |
| Triangle is largest black shape vs. circle is largest black shape. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP981 |
| Each column is assigned something independently; each row is assigned something independently; there is a rule that generates contents of squares from the row information and column information vs. there is a different kind of rule. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
To clarify the solution with an example: on the left is an image of a grid where the first row features a square with three dots and a square with nine dots, and the second row features a square with four dots and square with sixteen dots. "Three" and "four" are assigned to the rows; "x" and "x squared" are assigned to the columns.
To word the solution with mathematical jargon, "defines a (simply described) map from the Cartesian product of two sets vs. not so." Another equivalent solution is "columns (alternatively, rows) illustrate a consistent set of one-input operations." It is always possible to imagine the columns as inputs and the rows as operations and vice versa.
Left examples are a generalized version of the analogy grids seen in BP361. Any analogy a : b :: c : d shown in a 2x2 grid will fit on the left of this Problem.
All examples show grids of squares with an image in each square, such that there is some "rule" the images within the grid obey. The "rule" might be about how the images must relate to their neighbors, for example.
There is a trivial way in which any example can be interpreted so that it fits on the left side: imagine each row is assigned the list of all the squares in that row and each column is assigned its number, counting from the left. But each grid has a clear rule that is simpler than this. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
See BP979 for use of similar structures but with one square removed from the grid. Examples on the left here with any square removed should fit on the left there.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP976 BP977 BP978 BP979 BP980 * BP982 BP983 BP984 BP985 BP986
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
stub, convoluted, teach, structure, rules, grid, miniworlds
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
analogy (info | search)
|
|
|
WORLD
|
grid_of_images_with_rule [smaller | same | bigger]
zoom in left (grid_of_operations)
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP988 |
| Number of dots is a power of 2 vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP989 |
| Number of dots is n factorial for some n vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP993 |
| Net corresponds do a unique solid vs. net can be folded into multiple different solids. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
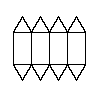
| BP994 |
| Net corresponds to a solid that can tessellate 3D space vs. net does not correspond to a solid that can tessellate 3D space. |
|
| ?
 |
|
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
More specifically these solids are polyhedra, and are often called "space-filling".
There is ambiguity here regarding some nets that can be folded to make multiple different solids. For example EX8175 could correspond to a cuboid with a pyramid-like protrusion at each end, a protrusion at one end and an indent at the other, or 2 indents. Only the second of these options can tessellate 3D space. For clarity's sake examples like this are not sorted on either side. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP989 BP990 BP991 BP992 BP993 * BP995 BP996 BP997 BP998 BP999
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
stub, precise, 3d, perfect, preciseworld
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
3d_net (info | search),
3d_solid (info | search)
|
|
|
WORLD
|
polyhedron_net [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Leo Crabbe
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP999 |
| The collection of collections obeys the same rule as the individual collections vs. it does not. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
Rhetorical question: Where would the collection of left examples of this Bongard Problem be sorted by this Bongard Problem? (The question is whether these examples considered together satisfy the pattern that all the parts do, namely that the whole satisfies the pattern that all the parts do.)
See BP793 and BP1004 for similar paradoxes. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
See BP1005 for the version about only numerical properties; examples in that BP would be sorted the same way here that they are there.
See BP1003 for a similar idea. Rather than the collection of collections imitating the individual collections, BP1003 is about the total combined collection imitating the individual collections. A picture showing (for example) an odd number of even-numbered groups would be sorted differently by these two BPs.
Also see BP1004, is likewise about the whole satisfying the same rule as its parts, but there the parts don't themselves have to be collections; there the parts are just plain individual objects. The panels in BP999 (this BP) should be sorted the same way in BP1004.
See BP1002, which is about only visual self-similarity instead of more general conceptual "self-similarity".
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP994 BP995 BP996 BP997 BP998 * BP1000 BP1001 BP1002 BP1003 BP1004
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
nice, stub, abstract, creativeexamples, left-narrow, rules, miniworlds
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
recursion (info | search),
self-reference (info | search)
|
|
|
WORLD
|
[smaller | same | bigger]
zoom in left | zoom in right
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP1082 |
| Shapes are congruent if (and only if) they are enclosed in the same space vs. not so. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
Welcome |
Solve |
Browse |
Lookup |
Recent |
Links |
Register |
Contact
Contribute |
Keywords |
Concepts |
Worlds |
Ambiguities |
Transformations |
Invalid Problems |
Style Guide |
Goals |
Glossary
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|