Search: keyword:structure
|
| |
|
| BP880 |
| Non-overlapping sides (patterns are disjoint) vs. possible object(s) could fit in overlap of sides (patterns intersect). |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP881 |
| Right pattern is "part of" left pattern (proper subset) vs. right pattern is not subset of left pattern. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP893 |
| As one quantity increases an equally obvious opposite quantity decreases vs. there is only one obvious quantity, which increases as the sequence progresses right. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
Another way of phrasing the solution: "Neither direction would more naturally be called increase in quantity vs. rightward progression would be called an increase."
Most right examples shown are unboundedly increasing, since finite sequences showing a quantity increasing usually also suggest "distance to end of sequence" as a decreasing opposite quantity. Even so, there are some finite sequences with one direction more intuitively increase-like than the other. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP888 BP889 BP890 BP891 BP892 * BP894 BP895 BP896 BP897 BP898
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
creativeexamples, structure, rules
|
|
|
WORLD
|
constant_change_seq_increase_right [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP894 |
| Examples fit solution (once it is known) relatively obviously vs. examples fit solution in subtle or complex, harder-to-see ways. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
One left and one right example with each solution are shown.
This BP is fuzzy for multiple reasons. How obvious it is that an example fits a rule is subjective. Also, somebody could read the simplicity of all included examples as part of a Bongard Problem's solution. For example, the more obvious version of "square number of dots vs. non-square number of dots" could be interpreted as "square small number of dots arranged in easy-to-read way vs. non-square small number of dots arranged in easy-to-read way."
Whether this Bongard Problem solution would categorize an image of itself left or right depends on the difficulty of the solutions of the mini-Problems. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
See keyword help.
See keyword hardsort.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP889 BP890 BP891 BP892 BP893 * BP895 BP896 BP897 BP898 BP899
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
fuzzy, abstract, notso, subjective, meta (see left/right), miniproblems, creativeexamples, presentationmatters, assumesfamiliarity, structure, contributepairs
|
|
|
WORLD
|
boxes_bpimage_three_per_side [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP917 |
| Reversible transformations vs. non-reversible transformations. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP951 |
| Process described leaves some inputs invariant vs. no output will resemble its input. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
There are many ambiguities here. The solver is expected to determine what things are "allowed" to be inputs for each process. To avoid confusion examples should not be sorted differently if you consider inputting nothing.
In each example there is at least some overlap between the set of possible inputs and the set of possible outputs for each process. If we did not apply this constraint, an easy example to be sorted right would be a process that turns blue shapes red.
A harder-to-read but more clearly defined version of this Problem could include within each example a mini Bongard Problem sorting left all allowed inputs for the process. |
|
|
REFERENCE
|
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fixed_point_(mathematics) |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP946 BP947 BP948 BP949 BP950 * BP952 BP953 BP954 BP955 BP956
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
structure, rules, miniworlds
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
function (info | search)
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Leo Crabbe
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP955 |
| Images of Bongard Problems that sort an image of their left side on their left and an image of their right side on their left vs. images of Bongard Problems that sort an image of their left side on their right and an image of their right side on their right. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP950 BP951 BP952 BP953 BP954 * BP956 BP957 BP958 BP959 BP960
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
abstract, dual, handed, leftright, solved, meta (see left/right), miniproblems, creativeexamples, assumesfamiliarity, structure, experimental
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
self-reference (info | search)
|
|
|
WORLD
|
oblong_boxes_bpimage_sorts_both_sides_skewed [smaller | same | bigger]
zoom in left (oblong_boxes_bpimage_sorts_both_sides_left) | zoom in right (oblong_boxes_bpimage_sorts_both_sides_right)
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Leo Crabbe
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP957 |
| Images of Bongard Problems that sort an image of their left side on their left and an image of their right side on their right vs. images of Bongard Problems that sort an image of their left side on their right and an image of their right side on their left. |
|
| |
|
| |
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP968 |
| Valid Bongard Problem vs. invalid Bongard Problem. |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
"Invalid Bongard Problems" are images that look sort of like Bongard Problems but aren't actually Bongard Problems.
With many examples included, this Problem might be placed somewhere to nonverbally show someone the subtler rules about what is allowed and what isn't allowed in Bongard Problems.
See BP829 for the Bongard Problem about Bongard Problems with no clear solution. |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
See BP522 (flipped) for a version with links to pages on the OEBP instead of images of Bongard Problems (miniproblems).
See BP829 (flipped) for a near exact copy of this Bongard Problem idea but that does not include images with two of the same boxes on either side.
Also see BP1080, which includes various different formats of Bongard Problems, distinguishing them from arbitrary images that are not Bongard Problems.
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP963 BP964 BP965 BP966 BP967 * BP969 BP970 BP971 BP972 BP973
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
teach, meta (see left/right), miniproblems, assumesfamiliarity, structure
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Jago Collins
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
| BP979 |
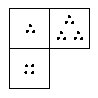
| It is possible to deduce the contents of the missing square vs. not so. |
|
| ?
 |
|
|
|
|
|
COMMENTS
|
All examples show grids of squares with an image in each square, such that there is some "rule" the images within the grid obey. The "rule" can be about how the images relate to their neighbors, it can involve the position of the images in the grid, and it can involve properties of the grid considered as a whole. One square from somewhere along the edge of the grid is removed.
Intentionally left out of this Problem (shown above sorted ambiguously) are cases in which the rule is not possible to deduce without seeing more squares. Due to this choice to omit those kinds of examples from the right, another acceptable solution to this Problem is "it is possible to deduce the contents of the missing square once the underlying rule is understood vs. not so." |
|
|
CROSSREFS
|
Adjacent-numbered pages:
BP974 BP975 BP976 BP977 BP978 * BP980 BP981 BP982 BP983 BP984
|
|
|
KEYWORD
|
structure, rules, miniworlds
|
|
|
CONCEPT
|
convey_enough_information (info | search),
choice (info | search)
|
|
|
WORLD
|
grid_of_images_with_rule_one_on_edge_missing [smaller | same | bigger]
|
|
|
AUTHOR
|
Aaron David Fairbanks
|
| |
|
|
Welcome |
Solve |
Browse |
Lookup |
Recent |
Links |
Register |
Contact
Contribute |
Keywords |
Concepts |
Worlds |
Ambiguities |
Transformations |
Invalid Problems |
Style Guide |
Goals |
Glossary
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|